Here are the relevant materials in United States v. Brown (N.D. Okla.):
Here are the relevant materials in United States v. Brown (N.D. Okla.):
Lesson — always bring your copy of Cohen. . . .


From the court:
The federal murder trials of two men charged with killing Osage Indians in the early 1920’s will be featured in a seminar and exhibit opening December 7 at the Old U.S. Post Office Building and Courthouse. Presented by the Historical Society of the U.S. District Court for the Western District of Oklahoma, “The Osage Reign of Terror: The Untold Legal History” tracksthe murders of wealthy Osage tribal members, the arrival of agents with the Bureau of Investigation who investigated, and the Federal Prosecutors who charged William K. Hale and John Ramsey with a number of the murders. The federal trials that followed resulted in a landmark Supreme Court ruling, charges of witness and juror tampering, and high courtroom drama. The events took place in Fairfax, Pawhuska, Guthrie and Oklahoma City and are featured in a book and movie of the same name, “Killers of the Flower Moon.”
A reception hosted by the Historical Society and featuring a documentary film about the trials as well as Federal Court and Osage dignitaries will be held on December 7 at 4 pm in the Federal Judicial Learning Center and Museum. The event is co-sponsored by the Bank of Oklahoma and The Federal Bar Association – Oklahoma City Chapter. The exhibit is open to the public beginning December 8, 2023, through October 2024.
Email Leigh Dudley, Executive Director at leigh@fjlcm.org or Arvo Mikkanen arvo.mikkanen@usdoj.gov for more information. Contact via text at 405/697-6117 or 405/420-9912.
Justice Sandra Day O’Connor was a true trailblazer, serving as the first woman Supreme Court Justice and she was a rare Westerner on the Court, but she was hardly a maverick. SOC’s story is dominated by two related characteristics about her political and legal life. First, she was a politician before she was a judge, likely leading to her judicial style that featured a heavy emphasis on compromise and policy-oriented judging. One would be surprised to find bright-line rules in her decisions. Second, she was naturally the key swing justice throughout most of the Rehnquist Court. She was certainly conservative, but she was open to hearing and respecting the other side. One would be hard-pressed to find anyone who really detested her.
That said, SOC absolutely owed this country an apology for her role in the federalism revolution that dominated the Rehnquist Court. Bill Rehnquist, who SOC dated in law school, led a federalism revolution that was plainly designed to destroy the Reconstruction era civil rights amendments and their Warren Court era enablers. It completely worked. Civil rights law in the US is completely dead unless you’re not brown or poor. SOC voted along with all of this.
SOC’s Indian law legacy contains elements of her judicial practices and philosophy but also intense deviations from her public image. Excepting one area of Indian law, SOC was not an existential threat to tribal interests (unlike at least a couple of her Rehnquist Court-era colleagues and her replacement on the Court), but she was not much of a friend to Indian country. The Rehnquist Court was an utter and total disaster for Indians and tribes, and SOC just went along with it.
Here is some raw data: (1) SOC voted against tribal interests in 48 out of 72 cases, exactly 2/3 of the time (excluding, as always, cases where there were competing Indian/tribal interests like Babbitt v. Youpee).; (2) SOC wrote a mere eight majority opinions and a just a few separate writings, probably because (3) SOC was in the majority in all but four cases between 1982 and 2005, or about 94 percent of the time. As a relatively unreliable conservative and a swing justice, she was probably too busy in “important” cases to write in Indian law, ala Scalia.
I’d characterize SOC’s Indian law legacy as featuring, (1) reflexive, often careless, deference to states’ rights, punctuated by two excellent decisions rejecting dumbass states’ rights positions; (2) personal conflicts of interest that had the potential to undermine western water law; (3) following alone with the majority rather than engaging with those who led; and (4) casual, hateful ethnocentrism.
First, states’ rights. Conservative justices have, for whatever reason, decided that federal Indian law is a contest between states’ rights and tribal interests, with the federal government an interested spectator (and occasional race traitor). How else can one explain why Slade Gorton as AG of the State of Washington argued Oliphant when there were zero states’ rights at play in that case?
In “states’ rights cases,” SOC started off strong, voting in favor of tribes 10 out of 15 cases from 1982’s Merrion through 1985’s Blackfeet Tribe case (doesn’t that seem like A LOT of cases?), but then (like the rest of the Court) she fell of an anti-tribal cliff. For the rest of her tenure, she voted in favor tribes at a state/local government’s expense a mere 4 times and against 28 times. Whoa! What a cruddy turnaround! Overall, that’s 14 in favor and 33 against, a 30 percent rate (a bit lower than her total vote percentage).
SOC’s first majority opinion, Rice v. Rehner, is the prototype states’ rights case. The Court held that tribal nations had no tradition of selling liquor tax free, therefore Indian traders in Indian country had to get a state liquor license. Hubba wa!?!? SOC voted against tribal interests in California v. Cabazon, Seminole Tribe v. Florida, and Nevada v. Hicks, cases you’ve probably heard of that were intensely important to Indian people and tribal nations.
SOC’s two reservation boundaries majority opinions, Hagen and Yankton, are prime examples of a policy-oriented, political compromise-seeking judging philosophy that somehow led to “states’ rights” victories. Though Congress had never expressly terminated either reservation, SOC found that demographic information about who lived there and owned the land was important, if not dispositive. These are two truly awful decisions that (a) did nothing to nail down any useful rules on reservation diminishment and (b) have been utterly repudiated by Nebraska v. Parker and McGirt. Hagen and Yankton figuratively are garbage cases (unlike Bourland which was literally a garbage case). [Related to the policy-oriented, compromise-seeking judging philosophy, see Brendale, a case where no one agreed but she forged a really weird compromise that never became the law.]
SOC wrote a concurring opinion in Nevada v. Hicks that deserves mention as well. That case involved tribal court jurisdiction over section 1983 claims against state police officers. No way was the Court going for that, but Scalia’s majority went full guns against tribal courts (aided by a truly awful concurrence from Souter), but SOC wrote separately in what Scalia suggested was effectively a dissent to say that the case wasn’t about tribal jurisdiction but instead was about state sovereign immunity. Thanks, I guess(?) in that SOC seemed repulsed by Scalia’s bigotry.
On the really good side, SOC wrote the majority opinion in Oklahoma Tax Commission v. Sac and Fox Nation. That decision, of course, was due in large part to Bill Rice’s brilliance, but perhaps also to the underwhelming performance of the OTC’s counsel:


SOC also wrote the majority in Minnesota v. Mille Lacs, truly an impressive achievement in favoring the law over crazy-racist shit from her colleagues. In a 5-4 majority where the dissent included all her conservative colleagues telling her was stupid for not relying on the terrible case Ward v. Race Horse, she affirmed Indian treaty fishing rights. All she was doing was following the law (it’s treaty rights after all) but the vicious anti-Indian onslaught of Rehnquist, Scalia, Kennedy, et al must have made her pause in a couple ways. Mille Lacs was the precursor to Herrera, where Justice Sotomayor finally killed Ward. The conservatives are still trying to make Ward v. Race Horse the law (hint: it never was, nor can it be). Pbbbt.
Second, personal conflicts of interest. Federal lawyers digging through the Nation Archives figured out that SOC almost wrote a 5-4 majority opinion eviscerating the Winters rights doctrine in Wyoming v. US (the Big Horn River adjudication), but then recused at the last minute — she was part-owner of her family ranch, which had been named a party in the Gila River general stream adjudication in Arizona. She really could have made her family business a tidy sum by gutting Winters rights, eh?

Some years later, in the 2000 incarnation of Arizona v. California, SOC dissented because (a) she chose to vote despite likely continuing conflicts of interest and (b) of course she did.
Third, SOC’s Indian law legacy was leading from behind. Unlike Whizzer White or Gorsuch, westerners who work hard to elevate Indian law to a place of prominence in the Court’s work, SOC was more of a Rehnquist/Kennedy westerner, tolerant of the existence of Indians (so long as they didn’t mess with her ranching interests) and hardly as a friend (Whizzer White wasn’t, either) — also not particularly interested in tribal rights.
Finally, SOC was not adverse to delving into casual cruelty toward Indian people. She wrote Lyng after all, quite possibly one of the most virulent anti-Indian decisions of the history of the Supreme Court that gave Justice Brennan an easy opportunity to write an empathetic dissent not riddled with demeaning and casually cruel language about poor people of color.
One last note — SOC (along with Justice Breyer) visited Indian country at the invitation of national tribal leaders back in 2001. Some have said SOC’s voting patterns changed as a result of that visit. There may be some validity to that theory. She voted against tribal interests 2/3 of the time, but after that visit, she voted in favor of tribal interests in 5 out of 8 cases (Chickasaw, where did wrote a rare dissent, White Mountain, adding the fifth vote over the votes of her buddies, Navajo I, Lara, and Cherokee v. Leavitt, we lost her in Inyo), but two of those negative votes were in Sherrill and Wagnon, a pair of wretched cases decided after Rehnquist’s death when SOC agreed to stay on as a lame duck judge. Kinda looks like she just gave up thinking and decided to channel whomever Bush W was going to appoint. Blech (it was Alito, who also visited Indian country — look what that gets us). Those cases were instances where the Court changed settled law in order to defeat tribal interests, so no thank you for those cases.
Being a judge is hard. SOC could have been a better one. She could have been a worse one. If I had to rate her (no one asked) in the recent pantheon of similar judges who retired or died since TT went online, I’d put ahead of RBG, behind Breyer, and way behind Stevens.
Here:
Remembering a Giant—Alex Tallchief Skibine
Elizabeth A. Kronk Warner
Second-Generation Source of Income Housing Discrimination
Armen H. Merjia
The Possible Futures of American Democracy
Jedediah Purdy
Religious Liberty, Discriminatory Intent, and the Conservative Constitution
Luke Boso
Tribal Cannabis Agriculture Law
Ryan B. Stoa
It Shouldn’t Be This Hard: The Law and Economics of Business in Indian Country
Adam Crepelle
Religious Freedom (for most) Restoration Act: A Critical Review of the Ninth Circuit’s Analysis in Apache Stronghold
Alex McFarlin
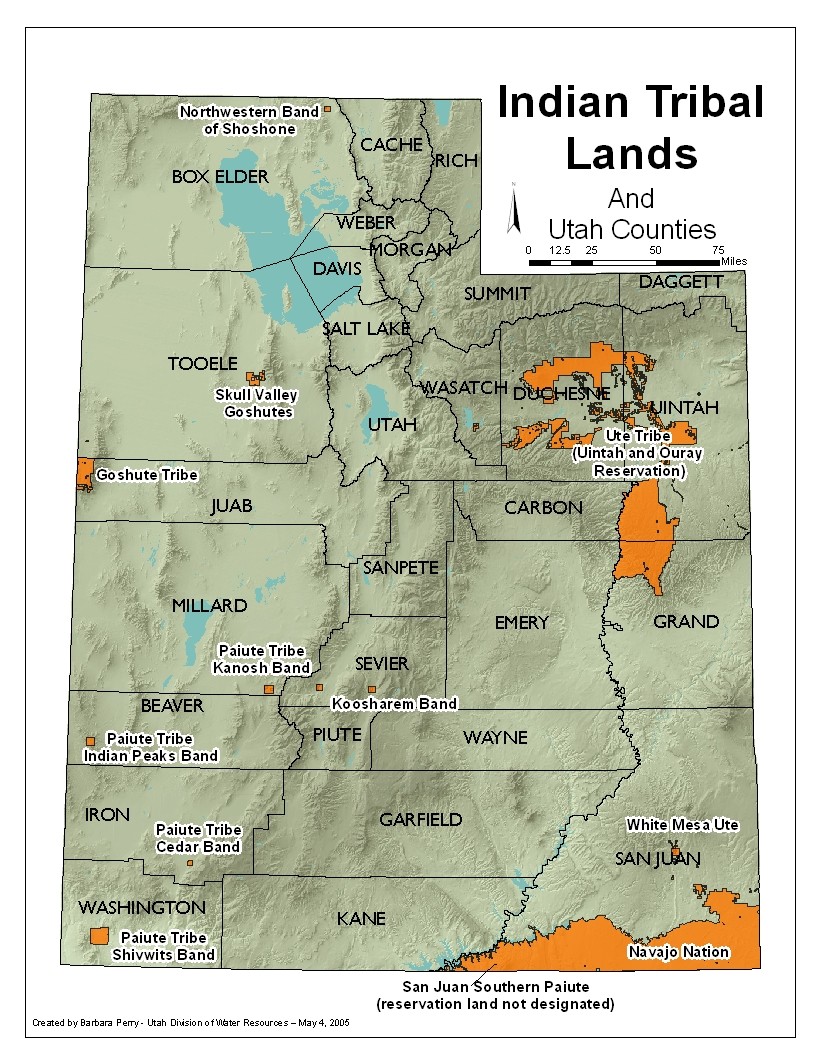
Here are the materials in Pueblo of San Felipe v. Haaland (D.N.M.):
32 Santa Ana Pueblo Motion to Intervene
33 San Felipe Opposition to 32

You must be logged in to post a comment.